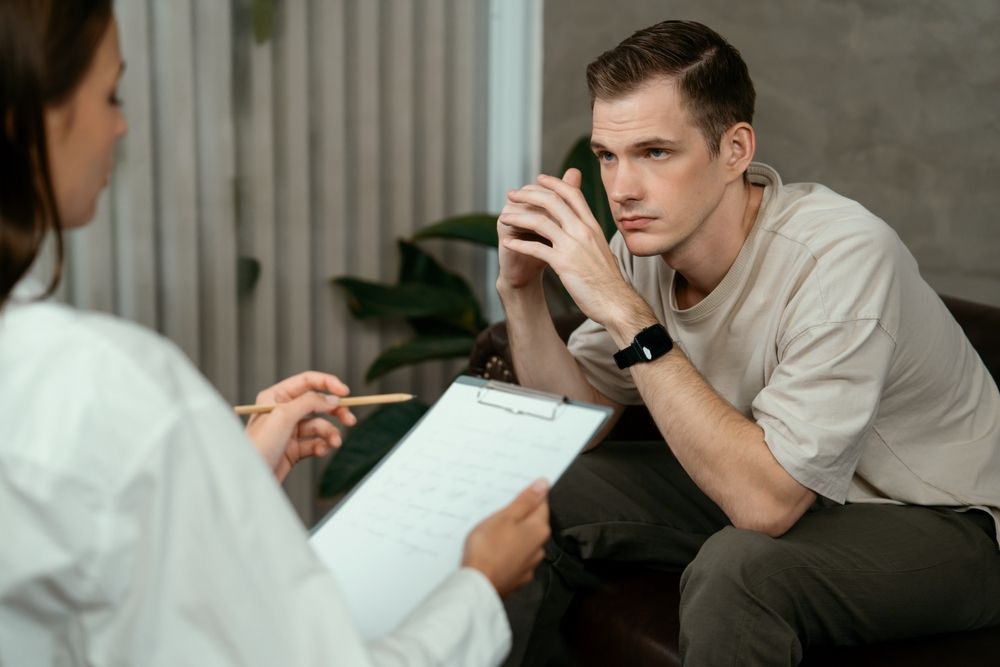
Antidepressants are a cornerstone in the treatment of mental health conditions, offering relief to individuals dealing with depression, anxiety disorders, and other related conditions. At Psychiatric Associate of Pennsylvania in Narberth, PA, experienced clinicians provide a personalized approach to ensure that patients find the right medication to address their needs. These medications work by altering brain chemistry to alleviate symptoms, improve mood, and enhance quality of life.
Depression and anxiety often arise from imbalances in neurotransmitters, the brain’s chemical messengers. Antidepressants target these imbalances, creating a foundation for recovery and emotional stability. For many individuals, these medications are life-changing, allowing them to engage in therapy, rebuild relationships, and regain control over their daily lives. While antidepressants are not a quick fix or universal solution, their role in comprehensive mental health care is significant and impactful.
Despite their widespread use, antidepressants remain misunderstood by many. Concerns about effectiveness, side effects, and stigma often create hesitation. However, with proper education and support from trained clinicians, patients can navigate these challenges and make informed decisions about their treatment. Antidepressants, when prescribed and managed appropriately, are a vital resource in addressing the complexities of mental health conditions.
How Antidepressants Work
Antidepressants work by targeting neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which regulate mood, energy levels, and overall mental well-being. These medications influence how neurotransmitters are absorbed, released, or broken down in the brain, helping restore balance and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. While the exact mechanisms vary depending on the medication, their primary goal is to address the root chemical imbalances contributing to mental health challenges.
For example, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine increase the availability of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation. By preventing serotonin from being reabsorbed too quickly, SSRIs allow it to remain active in the brain longer, improving emotional stability. Similarly, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) affect both serotonin and norepinephrine levels, addressing symptoms like low energy and poor concentration that are often associated with depression.
The effectiveness of antidepressants can vary from person to person, as individual brain chemistry and external factors influence how the body responds to treatment. Clinicians at Psychiatric Associate of Pennsylvania carefully evaluate each patient’s medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle to determine the most appropriate medication. Regular follow-ups and open communication are essential for monitoring progress and making any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Types of Antidepressants
Antidepressants are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different classes of medications are designed to target specific symptoms and conditions, providing tailored support for diverse mental health needs. SSRIs, including medications like sertraline and citalopram, are often the first-line treatment due to their efficacy and relatively mild side effects. These medications are particularly effective in treating depression, generalized anxiety disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
SNRIs, such as venlafaxine and duloxetine, are another common option. By increasing both serotonin and norepinephrine levels, these medications address a broader range of symptoms, including fatigue and physical pain often linked to depression. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), while less commonly prescribed due to their side effect profile, remain effective for treatment-resistant depression. These older medications influence multiple neurotransmitters and are sometimes used when newer drugs are not effective.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are another class of antidepressants that work by inhibiting the breakdown of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. Though effective, MAOIs require dietary restrictions to prevent adverse interactions, making them less common today. Atypical antidepressants, such as bupropion, offer unique mechanisms of action and are often used when traditional options do not yield desired results. The diversity of available antidepressants allows clinicians to craft highly personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
The Role of Clinicians in Antidepressant Treatment
Clinicians play an essential role in the safe and effective use of antidepressants. At Psychiatric Associate of Pennsylvania, the team emphasizes a collaborative approach, involving patients in every step of the decision-making process. This partnership begins with a thorough assessment of symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle factors to determine the most suitable medication.
Once treatment begins, clinicians closely monitor progress, assessing how well the medication addresses symptoms and identifying any potential side effects. Adjustments to dosage or switching medications may be necessary to optimize outcomes. Regular check-ins create a space for open dialogue, where patients can share their experiences and concerns. This ongoing communication ensures that treatment remains responsive and tailored to each individual’s evolving needs.
In addition to prescribing and managing medications, clinicians provide education about how antidepressants work, what to expect during treatment, and how to integrate them into a broader care plan. This guidance helps patients feel more informed and empowered, reducing uncertainty and promoting adherence to the prescribed regimen. By fostering trust and understanding, clinicians enable patients to take an active role in their mental health journey.
Addressing Concerns About Antidepressants
Starting antidepressants can be an intimidating step for many individuals, as misconceptions about these medications often fuel hesitation. Common concerns include fears of dependency, long-term side effects, and the belief that medications may alter one’s personality. Clinicians at Psychiatric Associate of Pennsylvania are committed to addressing these worries through education and support, ensuring that patients feel confident in their treatment decisions.
Antidepressants are not addictive, and their purpose is to stabilize mood rather than create dependency. While some medications may cause temporary side effects, such as nausea or fatigue, these often subside as the body adjusts. Clinicians work closely with patients to manage any discomfort, offering alternative options or dosage adjustments if necessary.
Another common misconception is that antidepressants suppress emotions or create an artificial sense of well-being. In reality, these medications aim to restore balance, allowing individuals to experience a full range of emotions without being overwhelmed by depression or anxiety. Education and open communication are key to demystifying antidepressants and helping patients understand their role in mental health care.
Integrating Antidepressants Into Holistic Care
While antidepressants are a powerful tool, they are most effective when integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan. Combining medication with therapy, lifestyle changes, and self-care practices creates a foundation for long-term recovery and emotional resilience. Clinicians at Psychiatric Associate of Pennsylvania emphasize the importance of this holistic approach, ensuring that patients receive well-rounded support.
Therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) help patients develop strategies for managing negative thought patterns and building healthier coping mechanisms. Physical activity, mindfulness, and proper nutrition further enhance mental well-being, complementing the effects of medication. By addressing the biological, psychological, and social dimensions of mental health, holistic care provides a robust framework for recovery.
Patients are encouraged to take an active role in their treatment, working alongside clinicians to explore additional avenues of support. This collaborative approach fosters empowerment, enabling individuals to reclaim control over their mental health and pursue a fulfilling life.
Sources:
Smith, K., & Cipriani, A. (2017). Antidepressants and Their Mechanisms of Action. The Lancet Psychiatry.
National Institute of Mental Health (2022). Mental Health Medications. National Institutes of Health.
Stein, M. B., & Craske, M. G. (2017). Treating Anxiety and Depression With Medications. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.